Demat accounts were introduced in India in 1996, before which shares and securities were physically issued and traded. The importance of opening a free Demat account is such that it allows the investors to hold their securities electronically in their Demat accounts. This makes the entire procedure of investing, holding, monitoring, and trading, faster, convenient, and cost-efficient.
Benefits of a Demat account
These are some of the advantages of a Demat account:
- Lower risks
- Easy holding
- Odd lots
- Reduced costs
- Reduced time
Details of these advantages are given below: 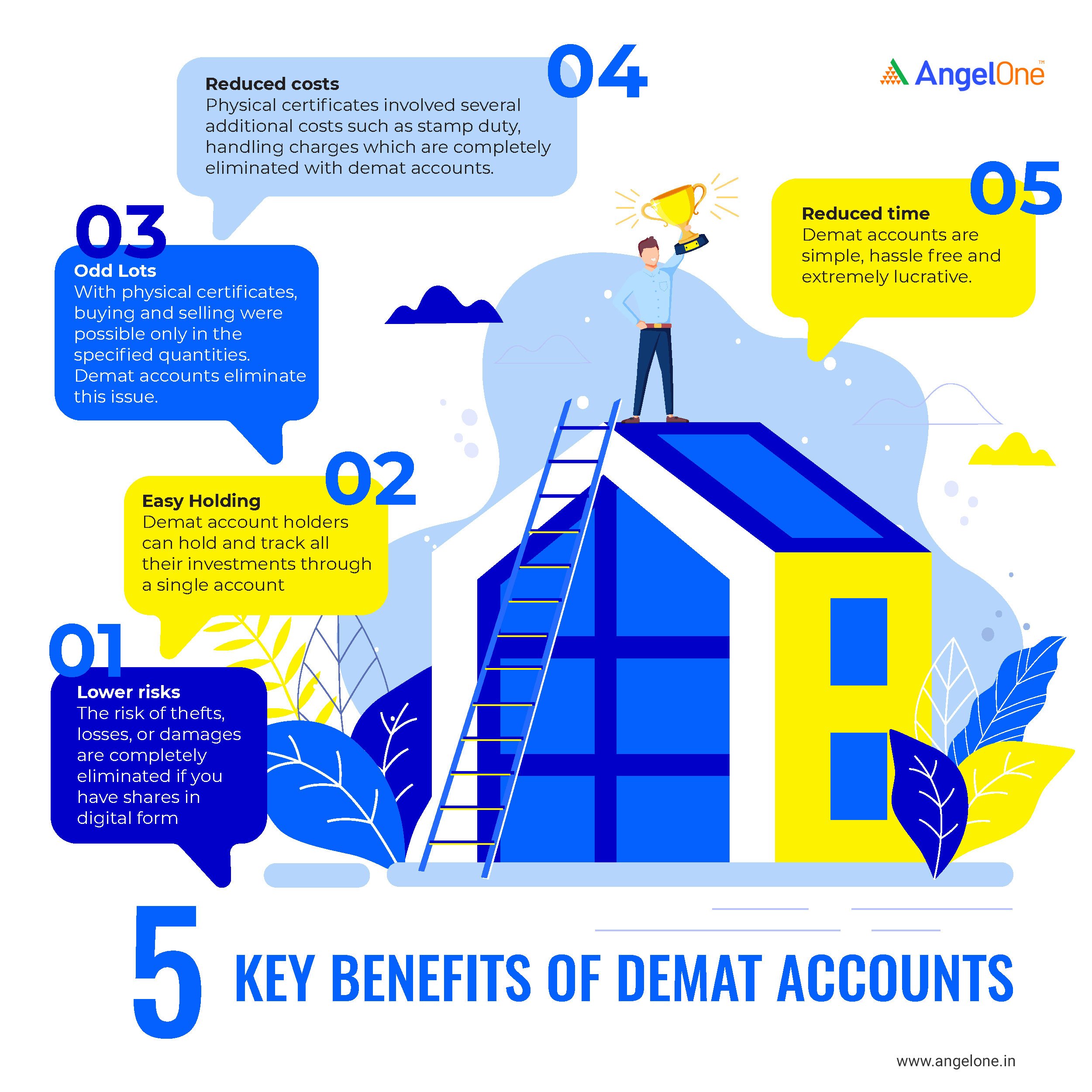
-
Lower risks:
Physical securities are risky due to thefts, losses, or damages. In addition, bad deliveries or fake securities pose further risks. These risks are eliminated with the opening of a Demat account, which provides holders with the option of holding all their investments in electronic form..
-
Easy holding:
Maintaining physical certificates is a tedious job. Moreover, keeping track of their performance is an added responsibility. Demat account holders can make it more convenient to hold and track all their investments through a single account.
-
Odd lots:
With physical certificates, buying and selling were possible only in the specified quantities. The convenience of dealing with odd lots or single security was also not available. Demat accounts eliminate this issue.
-
Reduced costs:
Physical certificates involved several additional costs, such as stamp duty, handling charges, and other such expenses. These extra expenses are eliminated with Demat accounts.
-
Reduced time:
Due to the elimination of paperwork, the time required in completing a transaction gets reduced. The reduced time requirement enables the account holder to make more purchases and sales of security holdings in a shorter time and with greater efficiency.
Demat accounts are simple, fuss-free and extremely lucrative. In today’s day and age, they are a must for financial planning.
Why do you need a Demat account?
The conversion of physical securities to electronic form is optional because an investor is allowed to hold securities either in physical or electronic format. However, monitoring physical certificates is more difficult compared to its dematerialised counterparts. Additionally, it is difficult to buy or sell securities in physical form. The number of agents dealing in physical shares, as well as the number of buyers willing to purchase physical shares, is much less compared to the individuals transacting in dematerialised securities.
Features of Demat account
-
Easy share transfers:
Investors can transfer their holdings through a delivery instruction slip (DIS) or receipt instruction slip (RIS) for buying or selling shares. These slips allow users to provide all the details that are required for executing a transaction smoothly.
-
Faster dematerialisation & rematerialisation of securities:
Demat account holders can provide instructions to their depository participant (DP) to convert physical certificates into electronic form. Alternatively, electronic securities can also be reconverted to physical form, if required.
-
Pledging facility to avail loan:
Several lenders provide loans against securities that are held in the Demat account of the borrowers. These holdings are used as collateral to avail loans by the account holders.
-
Freezing Demat accounts:
Demat account holders can freeze their accounts for a certain period, if required. This option can be beneficial if one wants to prevent unexpected debit or credit into one’s Demat account. The freezing option is also available for a specific quantity of securities held in the account.
-
Multiple accessing options:
Demat accounts are operated electronically, which means these can be accessed using multiple modes. These accounts can be accessed through the Internet using a computer, smartphone, or other smart devices.
-
SPEED E-Facility:
The National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) allows users to send instruction slips electronically instead of physically submitting the slip to the DP. This makes the procedure more convenient and less time-consuming.
-
Corporate benefits & actions:
If the companies offer dividends, refunds, or interest to their investors, these benefits are automatically available to the Demat account holders. In addition, corporate actions like bonus issues, right shares, or stock splits are automatically updated in the Demat account of all the shareholders.
Dematerialisation & Rematerialisation of Shares
-
Dematerialisation of shares:
The process of converting physical securities (shares, stocks, mutual fund units, bonds, debentures, etc.) into electronic form is known as the dematerialisation. Dematerialisation offers flexibility along with security and convenience. Holding share certificates in physical format carried risks like certificate forgeries, loss of important share certificates, and consequent delays in certificate transfers. Dematerialisation eliminates these hassles by allowing customers to convert their physical certificates into electronic format.
-
Rematerialisation of shares:
The process of converting electronic holdings of securities (shares, stocks, mutual fund units, bonds, debentures, etc.) into physical form (certificates) is known as rematerialisation. The procedure of rematerialisation involves the following steps:
- The account holder has to fill-up a Remat Request Form (RRF) and submit it to the Depository Participant (DP)
- After verifying the request, the DP forwards it to the depository and issues a signed and stamped acknowledgment slip to the holder
- The depository (NSDL or CDSL) then confirms this request to the company’s Share Transfer Agents
- Thereafter, the Share Transfer Agent prints these certificates and dispatches them to the holder and send a confirmation to the depository
- The DP sends a rematerialisation intimation to the account holder
Rights of a shareholder with dematerialised shares
The shareholders of dematerialised shares have the right to:
- Receive rights, shares, bonus, etc. if declared and approved
- Receive annual reports or any other periodical reports
- Receive dividends, if any, as approved
- Receive notices, postal ballot forms, and explanatory statements of general meetings
- Participate and vote at general meetings
- Demand statutory registers and documents for inspection during the working hours fixed by the company
- Demand poll on any resolution at general meetings
In general, a Demat shareholder enjoys similar rights as that of shareholders holding shares in physical form.

