
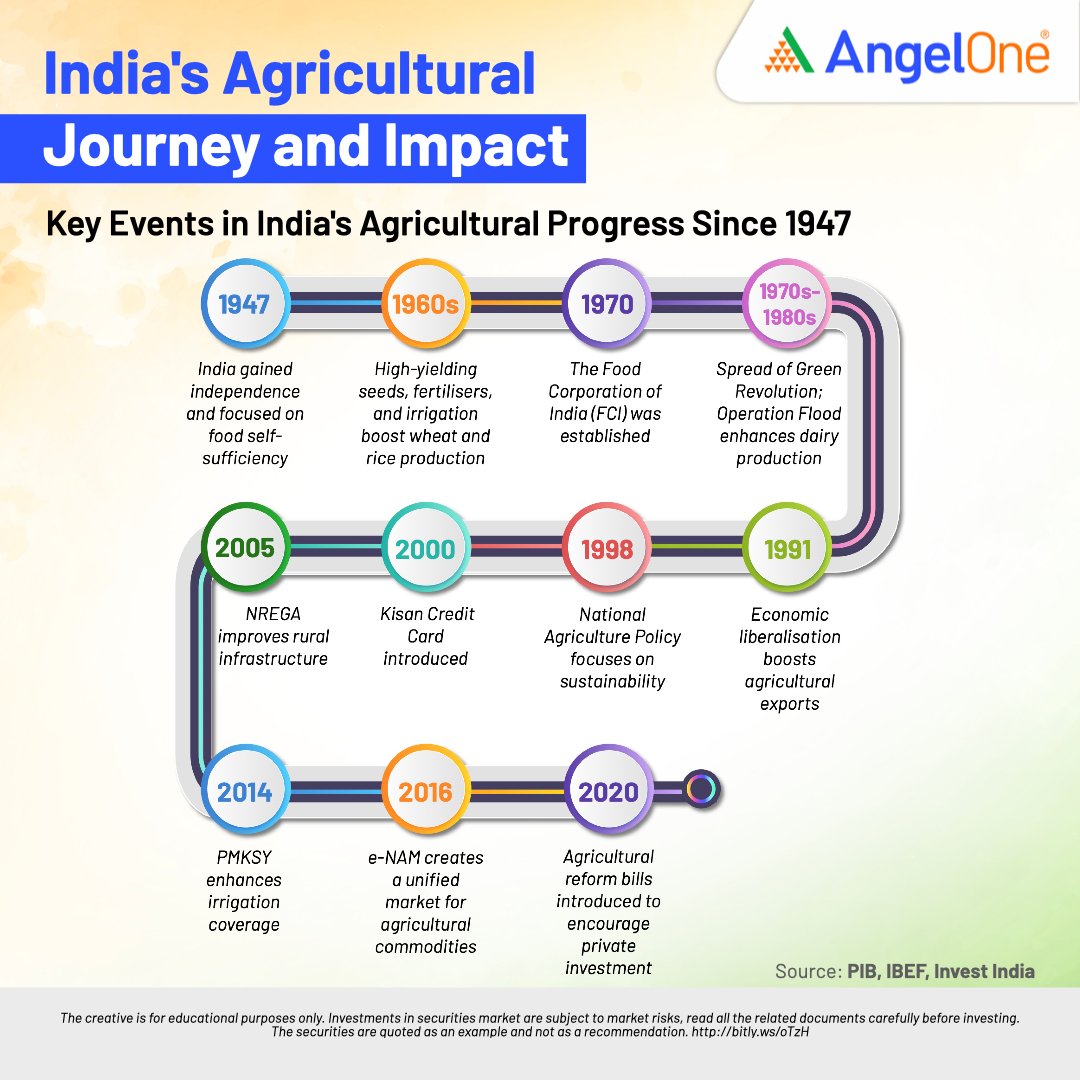
Indian agriculture, which began around 11,000 years ago with animal domestication and plant cultivation, has evolved significantly. Despite challenges like unpredictable weather, poor soil health, rising temperatures, and new pests, Indian agriculture has made remarkable progress thanks to advancements in science.
From 1950-51 to 2022, food grain production grew from 51 million tons to over 314 million tons. Other key areas also saw huge increases: horticultural crops by 11 times, fish by 18 times, milk by 10 times, and eggs by 53 times. This growth has greatly improved national food and nutrition security.
In 1950-51, India produced about 135 million tons of agricultural products. By 2021-22, production had risen to around 1,300 million tons, despite the area of land used for farming staying roughly the same at 140 million hectares.
India plays a major role in global agriculture and is the main source of income for about 55% of its population. The country has the world’s largest cattle herd, and it leads in the production of milk, pulses, and spices. India is also the second-largest producer of various crops and the second-largest exporter of sugar.
The food processing industry is a key part of the economy. It makes up 32% of the food market and ranks fifth in production, consumption, exports, and growth.
In the 2022-23 season, food grain production reached 330.5 million metric tons. India is the second-largest producer of food grains, fruits, vegetables, and sugar and is expecting to procure 521.27 million tons of rice for the 2023-24 season.
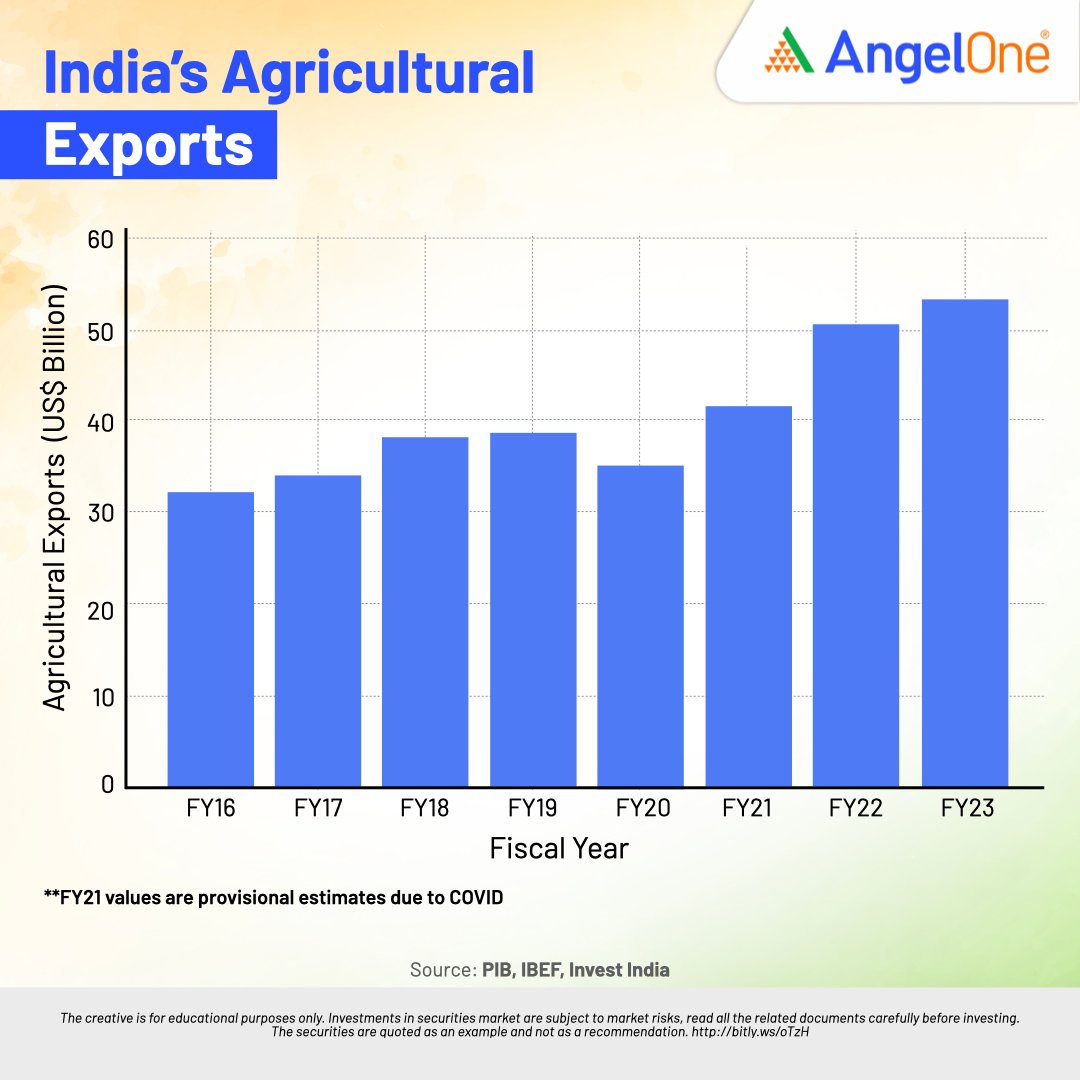
Recent investments and developments have boosted the sector. Foreign direct investment in agriculture services from April 2000 to March 2024 reached $3.08 billion. Agricultural and processed food exports totalled $35.18 billion in 2023-24. Key export items include marine products, rice, spices, buffalo meat, and sugar.
The agriculture sector is set to grow further with increased investment in infrastructure such as irrigation, warehousing, and cold storage. The use of genetically modified crops is expected to improve yields. India aims to become self-sufficient in pulses soon, thanks to new crop varieties and higher support prices.
The government plans to invest $9 billion in the fisheries sector in the next 5 years, aiming to increase fish production to 2.2 million tons by 2024-25. The adoption of food safety standards like ISO 9000 and HACCP will also benefit the food processing industry.
The Ministry of Food Processing Industries is working to boost investments in this sector. The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) scheme, which has an allocation of ₹4,600 crore (about $559.4 million), will continue until March 2026.
Indian agriculture has evolved impressively since independence, marked by significant increases in production and global influence. Future growth is anticipated through continued investment in infrastructure, technology, and food safety standards. With targeted investments and advancements in crop science, India is poised to enhance its agricultural output, achieve self-sufficiency in pulses, and maintain its leading role in the global food industry.
Disclaimer: This blog has been written exclusively for educational purposes. The securities mentioned are only examples and not recommendations. It is based on several secondary sources on the internet and is subject to changes. Please consult an expert before making related decisions.
Published on: Aug 19, 2024, 11:52 AM IST
We're Live on WhatsApp! Join our channel for market insights & updates
