
Since gaining independence in 1947, India’s defence sector has evolved significantly, transforming from a nascent industry into a formidable force with advanced technology and growing production capabilities. One of the reasons the Indian defence system has been able to attain its present reputation is the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), which was established in 1958.
Since its establishment, it has developed a range of programs and critical technologies, including missile systems, small and big armaments, artillery systems, electronic warfare (EW) systems, tanks, and armoured vehicles. This blog delves into the statistical milestones and developments that have shaped India’s defence sector over the decades.
Post-independence, India recognised the criticality of a robust defence sector for national security. Public sector undertakings (PSUs) like Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) were established to manufacture essential defence equipment. While these initial steps laid the groundwork, the sector faced limitations in technology and production capabilities.

By the 1970s, India’s defence budget had grown significantly, driven by the need for modernisation and the geopolitical climate.
India began to establish its indigenous defence production capabilities during this period. The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) was set up in 1958, leading to an increased focus on developing indigenous technology. LCA Tejas (Light Combat Aircraft) development began in the 1980s. The initial prototype flew in 2001, and the aircraft was officially inducted into the Indian Air Force in 2016.
The 1991 economic liberalisation boosted the defence sector. By the late 1990s, the budget had significantly increased.
India began to focus on increasing its defence exports. In 1991, defence exports were minimal. By 2000, they had grown to approximately $100 million.
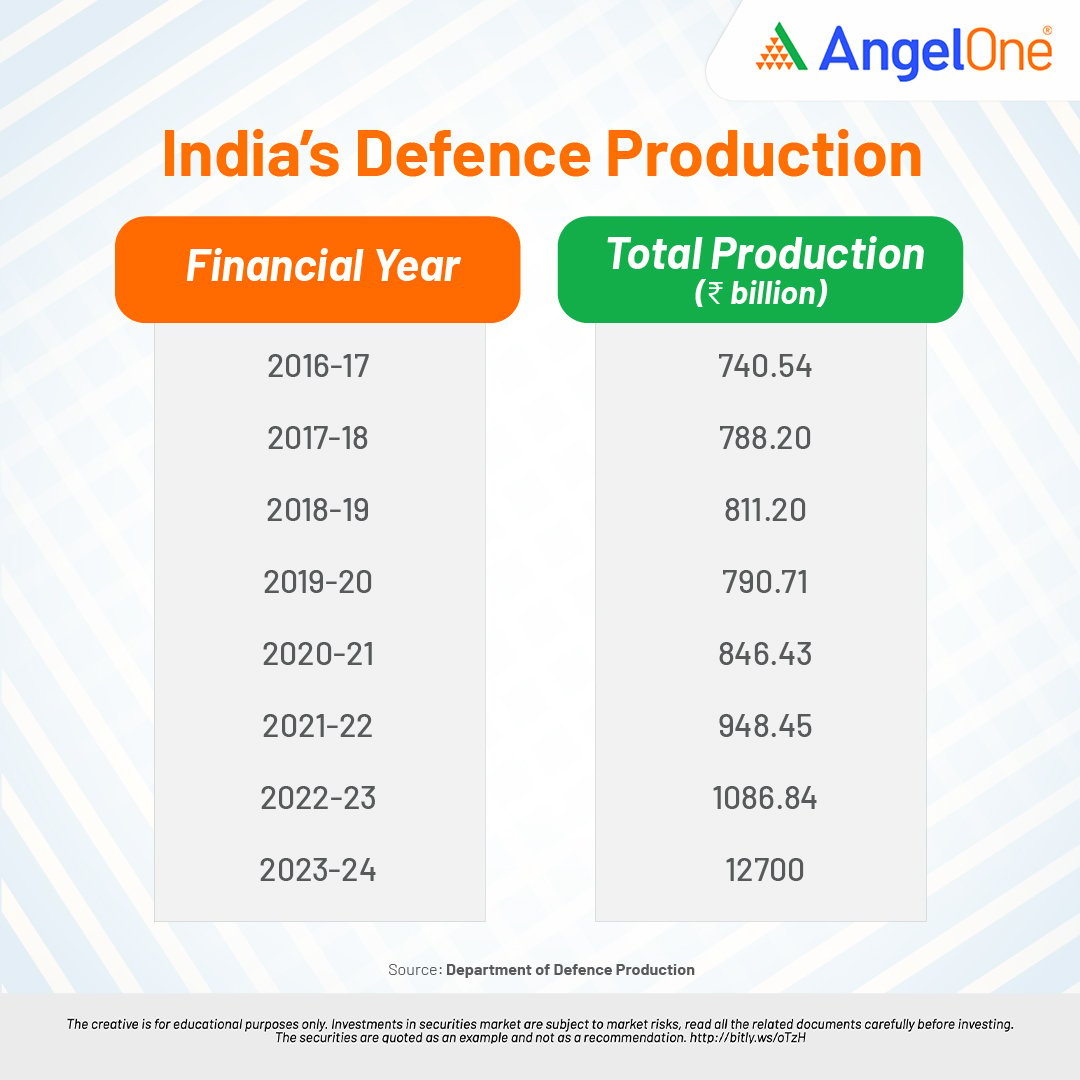
Since 1947, India’s defence sector has seen remarkable growth and modernisation. From a modest beginning with a limited budget and capacity, it has evolved into a high-tech industry with substantial investment in R&D and indigenous production capabilities. The sector’s progress is marked by increased budget allocations, growing defence exports, and significant achievements in indigenous defence technology. As India continues to enhance its defence capabilities, these statistical milestones highlight the sector’s trajectory and future potential.
Disclaimer: This blog has been written exclusively for educational purposes. The securities mentioned are only examples and not recommendations. It is based on several secondary sources on the internet and is subject to changes. Please consult an expert before making related decisions.
Published on: Aug 14, 2024, 5:49 PM IST
We're Live on WhatsApp! Join our channel for market insights & updates
