The government needs money to function and taxes are one of the most important sources of the government’s income. The government levies taxes on various items ranging from consumer goods and electronics to fuel and liquor. Every individual earning above a certain limit has to pay income tax. But what is income tax? What is the difference between Income Tax and the Goods and Services Tax? It is important to have the knowledge of the types of taxes of India. For instance, income tax is a direct tax, while GST is an indirect tax. To understand the difference between direct and indirect taxes, it is important to know both of them.
What is a direct tax?
Direct taxes are the taxes that are paid to the authority that imposes it without any intermediary. These taxes cannot be transferred to any other entity and have to be paid directly. The Central Board of Direct Taxes under the Department of Revenue is responsible for direct taxes in India. It administers the collection of direct taxes and provides crucial inputs to the government.
Types of Direct Tax
- Income Tax: Income tax is one of the most common types of direct tax imposed on individuals, firms, and corporations based on their income levels. It is assessed by the government on the income earned by taxpayers in a financial year.
- Corporate Tax: Corporate tax is a direct tax levied on the profits earned by companies or corporations. The tax rate may vary depending on the size and type of the company.
- Capital Gains Tax: Capital gains tax is imposed on the profit earned from the sale of capital assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and precious metals. The tax is applicable on the difference between the purchase price and the selling price of the asset.
- Property Tax: Property tax is a direct tax levied on the owners of real estate properties, including land, buildings, and other immovable assets. The tax amount is usually based on the assessed value of the property.
- Inheritance Tax: Inheritance tax, also known as estate tax or death duty, is imposed on the transfer of assets from a deceased person to their heirs or beneficiaries. The tax rate may vary depending on the value of the inherited assets and the relationship between the deceased and the heir.
Pros and Cons of Direct Tax
Pros
- Progressive Taxation: Direct taxes are often progressive, meaning that individuals with higher incomes pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes, promoting income equality.
- Revenue Stability: Direct taxes provide a stable source of revenue for the government, helping to fund essential public services and welfare programs.
Cons
- Complexity: Direct taxes can be complex to administer and comply with, requiring extensive record-keeping and reporting by taxpayers.
Potential for Tax Evasion: High tax rates may incentivise tax evasion, leading to a loss of revenue for the government and undermining the effectiveness of the tax system.
Common direct taxes
Income tax: It is the tax imposed on the income of an individual in a financial year. The quantum of the tax depends on the income tax slab of the taxpayer. The government provides a number of tax incentives to individual employees.
Tax on capital gains: Whenever you sell an asset at a profit, you have to pay the capital gains tax. The tax has been categorised into two forms-long term capital gains tax or short-term capital gains tax.
What is indirect tax?
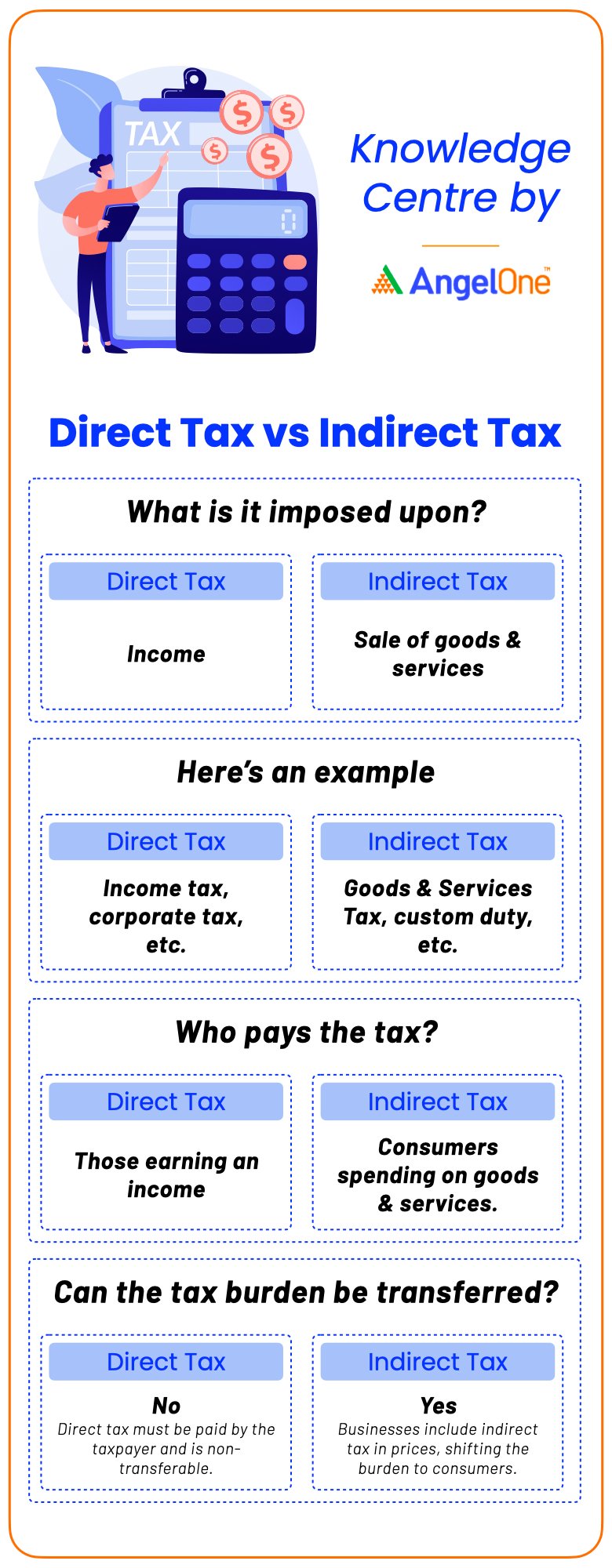
The differences between direct and indirect taxes are easily distinguishable. While direct tax is levied on income, indirect tax is imposed on goods and services and are paid through an intermediary. The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs is tasked with monitoring indirect taxes.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is one of the most common indirect taxes. When it was rolled out in 2017, it had subsumed over 17 indirect taxes such as service tax, central excise tax and state’s value-added tax. The GST council decides the rates at which different products and services are taxed.
Types of Indirect Taxes
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): GST is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services across India. It replaced various indirect taxes like central excise duty, service tax, VAT, etc., and aims to simplify the tax structure.
- Customs Duty: Customs duty is a tax imposed on goods imported into or exported out of a country. It is levied at specific rates and helps regulate trade by controlling the flow of goods across borders.
- Excise Duty: Excise duty is a tax levied on the manufacture or production of goods within the country. It is often included in the price of the product and collected from the manufacturer or producer.
- Service Tax: Service tax is imposed on certain services provided within the country. It is levied on the value of the service provided and collected from the service provider.
- Sales Tax: Sales tax is imposed on the sale of goods within a particular state or region. It is collected from the end consumer at the time of purchase.
Pros and Cons of Indirect Tax
Pros
- Indirect taxes are relatively easier to administer and collect compared to direct taxes.
- They are considered to be less intrusive as they are imposed on goods and services rather than directly on individuals or businesses.
- Indirect taxes can be used as a tool to regulate consumption patterns and promote certain industries or products.
Cons
- Indirect taxes tend to be regressive, impacting lower-income individuals disproportionately.
- They may lead to increased prices of goods and services, potentially causing inflationary pressures.
- Indirect taxes can sometimes be complex and difficult to understand, leading to compliance challenges for businesses and consumers alike.
Difference between direct tax and indirect tax
There are several major points that distinguish between direct and indirect tax.
Imposition: Direct tax is imposed on income and profits, while indirect tax is levied on goods and services.
Taxpayer: The individuals, companies and other taxable entities pay direct taxes, while indirect taxes are paid by the end-consumer.
Tax burden: Direct taxes like income tax are filed by the individual and hence the tax burden falls solely on them. In the case of indirect taxes like GST, the tax burden is transferred to consumers by manufacturers and service providers.
Transferability: One of the biggest differences between direct and indirect taxes is the transferability of the tax. Direct taxes cannot be transferred and have to be paid by self. Indirect taxes like GST can be transferred from one taxpayer to another.
Coverage: The coverage of direct taxes is not widespread as only an individual or entity earning above a certain limit is liable to pay direct taxes. On the other hand, indirect taxes have relatively larger coverage as they are uniformly imposed.
Inflation: Inflation is a crucial factor that distinguishes between direct and indirect taxes. Direct taxes can be used in controlling inflation. If the inflation rises beyond control, the government can increase direct taxes which will reduce money for sending and curtail demand for goods and services. Indirect taxes, on the other hand, lead to inflation. An increase in taxes leads to a rise in the cost of goods and services.
Nature: Direct tax is a progressive tax since it is imposed as per the income of an individual and not uniformly. A higher share of the burden of direct taxes is shared by affluent people. Indirect taxes are regressive in nature as everyone has to pay them irrespective of their income.
Conclusion
Both direct and indirect taxes are a crucial source of income for the government. In the long run, taxation has tended to decrease, giving more room for businesses and individuals to invest into the economy.

