What is Debt and Equity?
Debt is a financial instrument allowing one party to borrow lump sum funds from a second party. In return, the borrower repays the principal and interest over a specified timeline via periodically to the creditor. The borrower or debtor can invest the principal in their business or use it for other purposes while the lender gets the interest as a return over time. The borrowed funds are usually secured by assets, such as property, equipment, or financial assets.
Equity, on the other hand, refers to the value of the company's ownership or parts of it, called shares or stocks. These shares can be traded via over-the-counter deals between the company and investors or by selling shares on an exchange. The investors become shareholders and get a claim on the company's assets and earnings.
What is Equity Finance?
Equity finance refers to raising funds for a company by selling shares to investors. By selling equity, the company receives funds without incurring debt or the obligation to repay the investors. Equity investors become partial owners of the company and may receive a share of the profits.
For example, suppose a startup company with 9,000 shares in India decides to raise funds by offering 1,000 additional shares at Rs. 500 per share. If an investor purchases those 1,000 shares, they own 10% of the company, while the company receives Rs. 5,00,000 as capital.
Types of Equity Financing
- Angel investment: Angel investors invest in start-ups or small businesses. They typically invest small amounts of money in exchange for significant ownership in the business.
- Venture capital: Venture capital firms are professional investors who invest in early-stage and growth-stage businesses. They can invest larger amounts of money than angel investors.
- Crowdfunding: It is a way to raise money from many people, typically through online platforms. Crowdfunding can be used to raise money for various purposes, including starting a business or expanding an existing one.
- Initial public offering (IPO): An IPO is when a company sells its shares to the public for the first time. This is a way for companies to raise large amounts of money and gain access to a wider pool of investors.
Pros and Cons of Equity Financing
Pros
- Equity financing does not require the business to repay the money as debt, which can be a relief for struggling businesses.
- It can provide businesses with huge capital, which can be used to grow the business.
- It can help businesses attract experienced investors who can provide guidance and support.
- It can help businesses maintain their credit ratings.
Cons
- It dilutes ownership, which means that the founders and early investors give up some control of the business.
- Equity investors may have a say in how the business is run, which can be a challenge for entrepreneurs who are used to having full control.
- Equity investors may expect a return on their investment, which can put pressure on the business to perform well.
- Equity financing can be expensive, as investors typically require a share of the profits or a share of the company's assets in return for their investment.
What is Debt Finance?
Debt finance involves borrowing money from external sources with a commitment to repay the principal and the interest within a specified timeframe. Companies can obtain debt financing from banks and other financial institutions or by issuing corporate bonds to retail investors.
For instance, suppose a manufacturing company in India requires Rs. 10,00,000 to expand its operations. They approach a bank and secure a loan with an interest rate of 8% per annum. The company will be required to repay the loan and the interest over a predetermined period, usually through regular installments.
Types of Debt Financing
- Bank loans: These are loans provided by banks to businesses and individuals. The interest rates and repayment terms vary depending on the borrower's creditworthiness.
- Lines of credit: Lines of credit are a type of revolving credit that allows borrowers to access funds up to a certain limit. They are often used to finance short-term needs.
- Business credit cards: These credit cards are similar to personal credit cards. But the rewards and features serve businesses better.
Pros and Cons of Debt Financing
Here are some of the pros and cons of debt financing:
Pros
- Debt financing can offer businesses large amounts of capital quickly and easily.
- It does not dilute ownership, as is the case with equity financing.
- It can help businesses improve their credit ratings.
Cons
- It must be repaid with interest, which can be a significant financial burden.
- It can increase the risk of bankruptcy if the business is unable to make its payments.
- It can restrict the business's financial flexibility, as it may require regular payments regardless of financial performance.
- It can be expensive, as lenders typically charge higher interest rates for debt financing than equity financing.
What is the Difference Between Debt Financing and Equity Financing?
The following points help understand the difference between equity and debt financing:
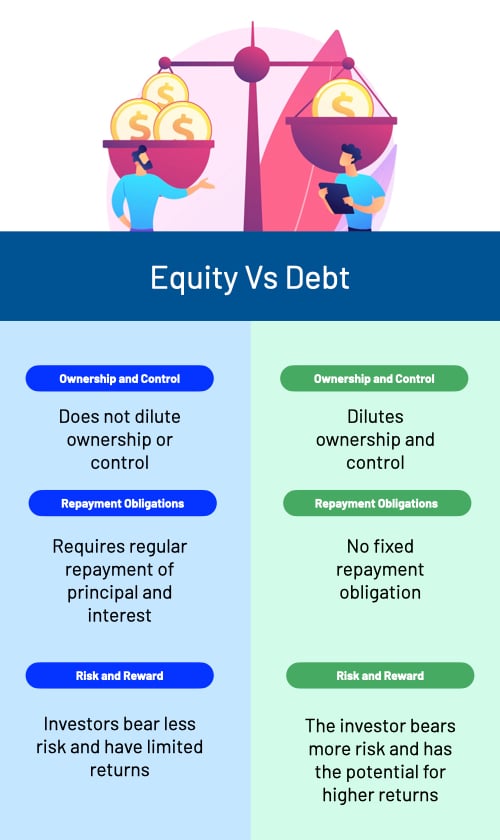
a. Ownership and Control
Debt financing does not dilute ownership or control of the company, as the borrowed funds are usually not tied to ownership rights. Only in the case of convertible bonds or debentures can a debt instrument be associated with an ownership interest.
Equity financing, however, involves the selling of ownership stakes, which dilutes the control of existing owners and gives new shareholders voting rights. At the company’s discretion, shareholders also receive dividends.
b. Repayment Obligations
Debt financing requires regular repayment of principal and interest according to the agreed terms. A company’s failure to repay its debt can have serious consequences, such as declaring bankruptcy and getting involved in legal troubles.
Equity financing does not have a fixed repayment obligation. However, in the long term, a company may pay its investors dividends regularly, which may be a burden on their finances. Moreover, the company's owners may still get into legal trouble if the money raised from investors is squandered without adequate reason.
c. Risk and Reward
Debt financing places the burden of repayment on the company, regardless of its profitability. The investor has less risk in the arrangement. However, the investor's returns also remain limited to the interest earned. The credit risk faced by the investor decreases with time as the amount left to be repaid decreases.
Equity financing requires the investor to share both the risks and rewards with the company. The risk stays for an extended period as a stock price crash can reduce the shareholders' wealth at any time. However, the investors can get much higher returns if the company grows its revenues and profits. A growing company benefits its owners in terms of appreciation of the share prices as well as dividends paid.
| Factors | Debt Financing | Equity Financing |
| Ownership and control | Does not dilute ownership or control. | Dilutes ownership and control. |
| Repayment obligations | Requires regular repayment of principal and interest. | No fixed repayment obligation. |
| Risk and reward | Investors bear less risk and have limited returns. | The investor bears more risk and has the potential for higher returns. |
Which Should You Choose: Debt vs Equity?
The choice between debt vs equity financing depends on several factors, including the following:
-
The Stage of Growth
At an early stage, a company may not have adequate sales and cash flow to guarantee a repayment schedule. Therefore, they might prefer to sell off some of their shares to one or more investors instead.
On the other hand, large, old companies are likely to have a steady cash flow and hence, they can afford to commit to regular repayments. Moreover, given the large market capitalisation that they have already reached, the investor is reluctant to pay such a large amount for shares as they fear, the growth in share price thereon may not be much.
The owner, too, is reluctant to give away shares worth a lot of money as well as control of the firm at a stage when the firm can make do with borrowings.
-
The Financial Situation
Between two equally big companies, the one with the more steady cash flow and confidence in future growth in revenues will be more likely to raise capital using debt. Moreover, the one whose ownership is highly diversified is also likely to prefer debt, as the existing owners may not want to dilute their holdings any further.
The likelihood of taking debt over equity also depends on the prevailing economic situation. For example, if investors are willing to pay more for the same percentage of shares, or if the existing interest rates for debt are too high, then the same company which was preferring debt financing last year, may prefer equity financing this year.
-
Risk Tolerance
The risks associated with equity and debt depends on whether you are the one making the investment or receiving it.
On the sell side, i.e., from the company’s point of view, equity financing is preferable for a risk-averse company as they do not have to repay anything anytime soon.
However, if the company’s finances are well-managed and its owners are more risk-taking, they may prefer taking debt rather than giving away equity. This is because the cost of debt is fixed at the interest amount. But the cost of giving away equity includes giving away the gains of the future from capital appreciation and dividends, which could be unlimited.
On the buy-side, i.e., from the investors' point of view, debt gives fixed low-risk returns (unless the bond is a floating rate or a convertible bond). Thus, if the investors find the company too risky, they might prefer to invest via debt over equity.
However, that does not mean that debt is risk-free. The company can go bankrupt and fail to repay its debt. Moreover, if the investors plan to sell the bonds, then a rise in the interest rates in the economy and a consequent fall in bond prices may harm them.
In comparison, equity may be more risky, but the profit potential is fairly high if the stocks are chosen wisely. Moreover, regular dividends can make a stock with a stagnant price attractive.
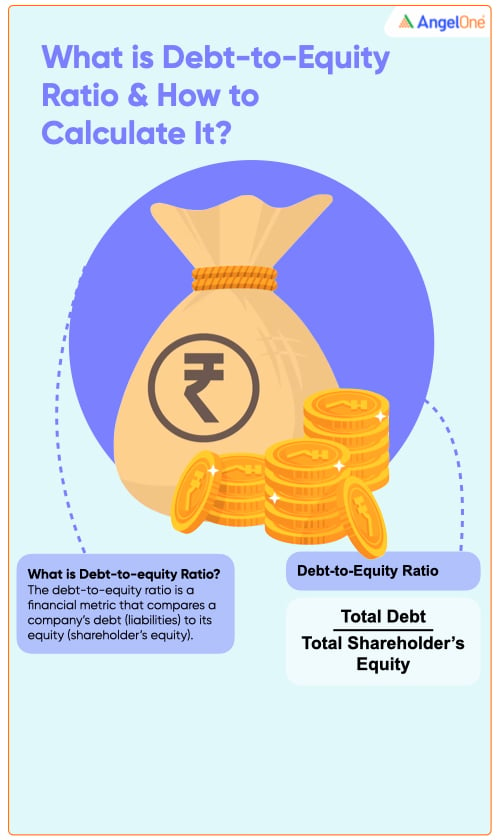
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio is a financial metric that compares a company's debt (liabilities) to its equity (shareholder's equity). It provides insights into a company's leverage and financial risk. A higher debt-to-equity ratio may suggest increased financial risk.
The formula for debt-to-equity ratio is the following:
Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt/Total Shareholder’s Equity
Whether a particular debt-to-equity ratio is good or not depends upon the specific industry that the company is in. For example, in a capital-intensive industry like shipbuilding, real estate development, or manufacturing, a higher debt-to-equity ratio will be more common compared to companies in the service sector.
Conclusion
Now that you know the difference between equity and debt, compare companies based on fundamentals like debt-to-equity ratios, interest coverage ratios, P/E ratios, etc. and think about which one you prefer to have in your portfolio. If you want to buy a stock, open a Demat account with Angel One, India’s trusted stockbroker.
Learn Free Stock Market Course Online at Smart Money with Angel One.
Explore the Share Market Prices Today
| IRFC share price | Suzlon share price |
| IREDA share price | Tata Motors share price |
| Yes Bank share price | HDFC Bank share price |
| NHPC share price | RVNL share price |
| SBI share price | Tata Power share price |